| Pugachev’s Rebellion | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||||
|
||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||
|
|
Coalition of Cossacks, Russian Serfs, Old Believers, and non-Russian peoples | |||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||
|
Catherine the Great Grigory Potemkin Petr Panin Alexander Suvorov Johann von Michelsohnen |
Yemelyan Pugachev Salawat Yulayev |
|||||
| Strength | ||||||
| 5,000+ men[2] |
1773:
1774:
|
|||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||
| 3,500 killed[2] |
|
Pugachev’s Rebellion (Russian: Восстание Пугачёва, romanized: Vosstaniye Pugachyova; also called the Peasants’ War 1773–1775 or Cossack Rebellion) of 1773–1775 was the principal revolt in a series of popular rebellions that took place in the Russian Empire after Catherine II seized power in 1762. It began as an organized insurrection of Yaik Cossacks headed by Yemelyan Pugachev, a disaffected ex-lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Army, against a background of profound peasant unrest and war with the Ottoman Empire. After initial success, Pugachev assumed leadership of an alternative government in the name of the late Tsar Peter III and proclaimed an end to serfdom. This organized leadership presented a challenge to the imperial administration of Catherine II.
The rebellion managed to consolidate support from various groups including the peasants, the Cossacks, and Old Believers priesthood. At one point, its administration claimed control over most of the territory between the Volga River and the Urals. One of the most significant events of the insurrection was the Battle of Kazan in July 1774.
Government forces failed to respond effectively to the insurrection at first, partly due to logistical difficulties and a failure to appreciate its scale. However, the revolt was crushed towards the end of 1774 by General Michelsohn at Tsaritsyn. Pugachev was captured soon after and executed in Moscow in January 1775. Further reprisals against rebel areas were carried out by General Peter Panin.
The events have generated many stories in legend and literature, most notably Pushkin’s historical novel The Captain’s Daughter (1836). It was the largest peasant revolt in the history of the Russian Empire.
Background and aims[edit]
As the Russian monarchy contributed to the degradation of the serfs, peasant anger ran high. Peter the Great ceded entire villages to favored nobles, while Catherine the Great confirmed the authority of the nobles over the serfs in return for the nobles’ political cooperation. The unrest intensified as the 18th century wore on, with more than fifty peasant revolts occurring between 1762 and 1769. These culminated in Pugachev’s Rebellion, when, between 1773 and 1775, Yemelyan Pugachev rallied the peasants and Cossacks and promised the serfs land of their own and freedom from their lords.
There were various pressures on Russian serfs during the 18th century, which induced them to follow Pugachev. The peasantry in Russia were no longer bound to the land, but tied to their owner. The connecting links that had existed between the peasant community and the tsar, which had been diminishing, was broken by the interposition of the serf owners; these private lords or agents of the Church or state who owned the land blocked serfs’ access to the political authority. Many nobles returned to their estates after 1762 and imposed harsher rules on their peasants. The relationship between peasant and ruler was cut off most dramatically in the decree of 1767, which completely prohibited direct petitions to the empress from the peasantry. The peasants were also subject to an increase in indirect taxes due to the increase in the state’s requirements. In addition, a strong inflationary trend resulted in higher prices on all goods.[4] The peasants felt abandoned by the «modern» state.[5] They were living in desperate circumstances and had no way to change their situation, having lost all possibilities for political redress.
There were natural disasters in Russia during the 18th century, which also added strain on the peasants. Frequent recurrence of crop failures, plagues and epidemics created economic and social instability. The most dramatic was the 1771 epidemic in Moscow, which brought to the surface all the unconscious and unfocused fears and panics of the populace.[6]
Each ruler altered the position of the Church, which created more pressure. Peter the Great gave the Church new obligations, while its administration assimilated to a department of the secular state. The Church’s resources, or the means of collection, could not meet the new obligations and as a consequence, they heavily exploited and poorly administered their serfs. The unrest spurred constant revolt among Church serfs.[6]
Leadership and strategy[edit]
Pugachev’s image according to folk memory and contemporary legends was one of a pretender-liberator. As Peter III, he was seen as Christ-like and saintly because he had meekly accepted his dethronement by his evil wife Catherine II and her courtiers. He had not resisted his overthrow, but had left to wander the world. He had come to help the revolt, but he did not initiate it; according to popular myth, the Cossacks and the people did that.[7]
The popular mythology of Peter III linked Pugachev with the Emancipation Manifesto of 1762 and the serf’s expectations of further liberalizations had he continued as ruler. Pugachev offered freedom from the poll tax and the recruit-levy, which made him appear to follow in the same vein as the emperor he was impersonating.
Pugachev attempted to reproduce the St. Petersburg bureaucracy. He established his own College of War with quite extensive powers and functions. He did not promise complete freedom from taxation and recruitment for the peasants; he granted only temporary relief. His perception of the state was one where soldiers took the role of Cossacks, meaning they were free, permanent, military servicemen. Pugachev placed all other military personnel into this category as well, even the nobles and officers who joined his ranks. All peasants were seen as servants of the state, they were to become state peasants and serve as Cossacks in the militia. Pugachev envisioned the nobles returning to their previous status as the czar’s servicemen on salary instead of estate and serf owners. He emphasized the peasants’ freedom from the nobility. Pugachev still expected the peasants to continue their labor, but he granted them the freedom to work and own the land. They would also enjoy religious freedoms and Pugachev promised to restore the bond between the ruler and the people, eradicating the role of the noble as the intermediary.[8]
Under the guise of Peter III, Pugachev built up his own bureaucracy and army, which copied that of Catherine. Some of his top commanders took on the pseudonyms of dukes and courtiers. Zarubin Chaika, Pugachev’s top commander, for example, took the guise of Zakhar Chernyshev. The army Pugachev established, at least at the very top levels of command, also mimicked Catherine’s. The organizational structure Pugachev set up for his top command was extraordinary, considering Pugachev defected as an ensign from Catherine’s army. He built up his own War College and a fairly sophisticated intelligence network of messengers and spies. Even though Pugachev was illiterate, he recruited the help of local priests, mullahs, and starshins to write and disseminate his «royal decrees» or ukases in Russian and Tatar languages. These ukazy were copied, sent to villages and read to the masses by the priests and mullahs. In these documents, he begged the masses to serve him faithfully. He promised to grant to those who followed his service land, salt, grain, and lowered taxes, and threatened punishment and death to those who didn’t. For example, an excerpt from a ukase written in late 1773:
From me, such reward and investiture will be with money and bread compensation and with promotions: and you, as well as your next of kin will have a place in my government and will be designated to serve a glorious duty on my behalf. If there are those who forget their obligations to their natural ruler Peter III, and dare not carry out the command that my devoted troops are to receive weapons in their hands, then they will see for themselves my righteous anger, and will then be punished harshly.[9]
Recruitment and support[edit]
From the very beginning of the insurgency, Pugachev’s generals carried out mass recruitment campaigns in Tatar and Bashkir settlements, with the instructions of recruiting one member from every or every other household and as many weapons as they could secure. He recruited not only Cossacks, but Russian peasants and factory workers, Tatars, Bashkirs, and Chuvash. Famous Bashkir hero Salawat Yulayev joined him. Pugachev’s primary target for his campaign was not the people themselves, but their leaders. He recruited priests and mullahs to disseminate his decrees and read them to the masses as a way of lending them credence.
Priests in particular were instrumental figures in carrying out Pugachev’s propaganda campaigns. Pugachev was known to stage “heroic welcomes” whenever he entered a Russian village, in which he would be greeted by the masses as their sovereign. A few days before his arrival to a given city or village, messengers would be sent out to inform the priests and deacons in that town of his impending arrival. These messengers would request that the priests bring out salt and water and ring the church bells to signify his coming. The priests would also be instructed to read Pugachev’s manifestos during mass and sing prayers to the health of the Great Emperor Peter III. Most priests, although not all, complied with Pugachev’s requests. One secret report of Catherine’s College of War, for example, tells of one such priest, Zubarev, who recruited for Pugachev in Church under such orders. “[Zubarev], believing in the slander-ridden decree of the villainous-imposter, brought by the villainous Ataman Loshkarev, read it publicly before the people in church. And when that ataman brought his band, consisting of 100 men, to their Baikalov village, then that Zubarev met them with a cross and with icons and chanted prayers in the Church; and then at the time of service, as well as after, evoked the name of the Emperor Peter III for suffrage.” (Pugachevshchina Vol. 2, Document 86. Author’s translation)
Pugachev’s army was composed of a diverse mixture of disaffected peoples in southern Russian society, most notably Cossacks, Bashkirs, homesteaders, religious dissidents (such as Old Believers) and industrial serfs. Pugachev was very much in touch with the local population’s needs and attitudes; he was a Don Cossack and encountered the same obstacles as his followers. It is noticeable that Pugachev’s forces always took routes that reflected the very regional and local concerns of the people making up his armies. For example, after the very first attack on Yaitsk, he turned not towards the interior, but instead turned east towards Orenburg which for most Cossacks was the most direct symbol of Russian oppression.
The heterogeneous population in Russia created special problems for the government, and it provided opportunities for those opposing the state and seeking support among the discontented, as yet unassimilated natives.[10] Each group of people had problems with the state, which Pugachev focused on in order to gain their support.
Non-Russians, such as the Bashkirs, followed Pugachev because they were promised their traditional ways of life, freedom of their lands, water and woods, their faith and laws, food, clothing, salaries, weapons and freedom from enserfment.[11] Cossacks were similarly promised their old ways of life, the rights to the river Iaik (now the Ural River) from source to sea, tax-free pasturage, free salt, twelve chetvi of corn and 12 roubles per Cossack per year.[11]
Pugachev found ready support among the odnodvortsy (single homesteaders). In the westernmost part of the region swept by the Pugachev rebellion, the right bank of the middle Volga, there were a number of odnodvortsy. These were descendants of petty military servicemen who had lost their military function and declined to the status of small, but free, peasants who tilled their own lands. Many of them were also Old Believers, and so felt particularly alienated from the state established by Peter the Great. They were hard-pressed by landowners from central provinces who were acquiring the land in their area and settling their serfs on it. These homesteaders pinned their hopes on the providential leader who promised to restore their former function and status.[12]
The network of Old Believer holy men and hermitages served to propagandize the appearance of Pugachev as Peter III and his successes, and they also helped him recruit his first followers among the Old Believer Cossack of the Iaik.[13]
The Iaik Cossack host was most directly and completely involved in the Pugachev revolt. Most of its members were Old Believers who had settled among the Iaik River. The Cossacks opposed the tide of rational modernization and the institutionalization of political authority. They regarded their relationship to the ruler as a special and personal one, based on their voluntary service obligations. In return, they expected the czar’s protection of their religion, traditional social organization, and administrative autonomy. They followed the promises of Pugachev and raised the standard of revolt in the hope of recapturing their previous special relationship and securing the government’s respect for their social and religious traditions.[14]
Factory workers supported Pugachev because their situation had worsened; many state-owned factories had been turned over to private owners, which intensified exploitation. These private owners stood as a barrier between the workers and the government; they inhibited appeals to the state for improvement of conditions. Also, with the loss of Russia’s competitive advantage on the world market, the production of the Ural mines and iron-smelting factories declined. This decline hit the workers the hardest because they had no other place to go or no other skill to market. There was enough material to support rebellion against the system. By and large the factories supported Pugachev, some voluntarily continuing to produce artillery and ammunition for the rebels.[15]
Challenge to the Russian state[edit]
In 1773 Pugachev’s army attacked Samara and occupied it. His greatest victory came with the taking of Kazan, by which time his captured territory stretched from the Volga to the Ural mountains. Though fairly well-organized for a revolt at the time, Pugachev’s main advantage early on was the lack of seriousness about Pugachev’s rebellion. Catherine the Great regarded the troublesome Cossack as a joke and put a small bounty of about 500 rubles on his head. But by 1774, the threat was more seriously addressed; by November the bounty was over 28,000 rubles. The Russian general Michelson lost many men due to a lack of transportation and discipline among his troops, while Pugachev scored several important victories.
Pugachev launched the rebellion in mid-September 1773. He had a substantial force composed of Cossacks, Russian peasants, factory serfs, and non-Russians with which he overwhelmed several outposts along the Iaik and early in October went into the capital of the region, Orenburg. While besieging this fortress, the rebels destroyed one government relief expedition and spread the revolt northward into the Urals, westward to the Volga, and eastward into Siberia. Pugachev’s groups were defeated in late March and early April 1774 by a second relief corps under General Bibikov, but Pugachev escaped to the southern Urals, Baskiria, where he recruited new supporters. Then, the rebels attacked the city of Kazan, burning most of it on July 23, 1774. Though beaten three times at Kazan by tsarist troops, Pugachev escaped by the Volga, and gathered new forces as he went down the west bank of the river capturing main towns. On September 5, 1774, Pugachev failed to take Tsaritsyn and was defeated in the steppe below that town. His closest followers betrayed him to the authorities. After a prolonged interrogation, Pugachev was publicly executed in Moscow on 21 January [O.S. 10 January] 1775.[16]
Indigenous involvement[edit]
Pugachev’s vague rhetoric inspired not only Cossacks and peasants to fight, but also indigenous tribes on the eastern frontier. These indigenous groups made up a comparatively small portion of those in revolt, but their role should not be underestimated. Each group had a distinct culture and history, which meant that their reasons for following Pugachev were different.
The Mordovians, Mari, Udmurts, and Chuvash (from the Volga and Kama basin) for example, joined the revolt because they were upset by Russian attempts to convert them to Orthodoxy. These groups lived within Russia’s borders, but held onto their language and culture. During the Pugachev Rebellion, these natives responded by assassinating Orthodox clergy members.[citation needed] Because the natives professed allegiance to Pugachev, the rebel leader had no choice but to implicitly condone their actions as part of his rebellion.[17]
The Tatars (from the Volga and Kama basin) were the indigenous group with the most complex political structure. They were most closely associated with Russian culture because they had lived within the empire’s borders since the 16th century. Many Tatars owned land or managed factories. As more integrated members of the Russian Empire, the Tatars rebelled in objection to the poll tax and their military and service obligations. The Tatars were closely associated with the Cossacks and were a crucial part of Pugachev’s recruitment efforts.
As a group, the Bashkirs had the most unified involvement in the rebellion. The Bashkirs were nomadic herdsman, angered by newly arrived Russian settlers who threatened their way of life. Russians built factories and mines, began farming on the Bashkir’s former land, and tried to get the Bashkirs to abandon their nomadic life and become farmers too. When fighting broke out, Bashkir village leaders preached that involvement in the rebellion would end Russian colonialism, and give the Bashkirs the political autonomy and cultural independence they desired. The Bashkirs were crucial to Pugachev’s rebellion. Some of the memorable leaders of the rebellion, like Salavat Yulaev were Bashkirs, and historian Alan Bodger argues that the rebellion might have died in the beginning stages were it not for the Bashkir’s involvement. In spite of their integral role, Bashkirs fought for different reasons than many of the Cossacks and peasants, and sometimes their disparate objectives disrupted Pugachev’s cause. There are accounts of Bashkirs, upset over their lost land, taking peasant land for themselves. Bashkirs also raided factories, showing their aggression towards Russian expansion and industrialization. Pugachev thought that these raids were ill-advised and not helpful towards his cause.
While the Bashkirs had a clear unified role in the rebellion, the Buddhist Kalmyks and Muslim Kazakhs, neighboring Turkic tribes in the steppe, were involved in a more fragmented way. The Kazakhs were nomadic herdsman like the Bashkirs, and were in constant struggle with neighboring indigenous groups and Russian settlers over land. Pugachev tried hard to get Kazakh leaders to commit to his cause, but leaders like Nur-Ali would not do so fully. Nur-Alit engaged in talks with both Pugachev’s and Tsarist forces, helping each only when it was advantageous for him. The Kazakhs mostly took advantage of the rebellion’s chaos to take back land from Russian peasants and Bashkir and Kalmyk natives. Historian John T. Alexander argues that these raids, though not directly meant to help Pugachev, ultimately did help by adding to the chaos that the Imperial forces had to deal with.[18]
The early Volga German settlements were attacked during the Pugachev uprising.
The Kalmyks’ role in the rebellion was not unified either, but historians disagree about how to classify their actions. Historian Alan Bodger argues that the Kalmyks’ role was minimal. They helped both sides in the conflict, but not in a way that changed the results. John T. Alexander argues that the Kalmyks were a significant factor in the rebel’s initial victories. He cites the Kalmyk campaign led by II’ia Arapov which, though defeated, caused a total uproar and pushed the rebellion forward in the Stavropol region.[19]
Defeat[edit]
By late 1774 the tide was turning, and the Russian army’s victory at Tsaritsyn left 9,000-10,000 rebels dead. Russian General Panin’s savage reprisals, after the capture of Penza, completed their discomfiture. By 21 August 1774, Don Cossacks recognize that Pugachev is not Peter III. By early September, the rebellion was crushed. Yemelyan Pugachev was betrayed by his own Cossacks when he tried to flee in mid-September 1774, and they delivered him to the authorities.[20] He was beheaded and dismembered on 21 January 1775, in Moscow.
After the revolt, Catherine cut Cossack privileges further and set up more garrisons across Russia. Provinces became more numerous, certain political powers were broken up and divided among various agencies, and elected officials were introduced.[21]
Assessments[edit]
The popular interpretation of the insurgency was that Pugachev’s men followed him out of the desire to free themselves from the oppression of Catherine’s reign of law. However, there are documents from Pugachev’s war college and eye witness accounts that contradict this theory. While there were many who believed Pugachev to be Peter III and that he would emancipate them from Catherine’s harsh taxes and policies of serfdom, there were many groups, particularly of Bashkir and Tatar ethnicity, whose loyalties were not so certain. In January 1774, for example, Bashkir and Tatar generals led an attack on the City of Kungur. During the revolt the nomadic Kazakhs took the opportunity to raid the Russian settlements.[22] Pugachev’s troops suffered from a lack of food and gunpowder. Many fighters deserted, including one general who left the battle and took his entire unit with him. One general wrote in a report to his superior, V. I. Tornova, «For the sake of your eminence, we humbly request that our Naigabitskiaia Fortress be returned to us with or without a detachment, because there is not a single Tatar or Bashkir detachment, since they have all fled, and the starshins, who have dispersed to their homes, are presently departing for the Naigabanskaia fortress.» (Dokumenty i Stavki E. I. Pugacheva, povstancheskikh vlastei i ucherezhdenii, 1773-1774. Moskva, Nauka, 1975. Document number 195. Author’s translation)
The concept of freedom was applied to the movement in regard to being free from the nobility. A peasant was to be free to work and own the land he worked. Pugachev’s followers idealized a static, simple society where a just ruler guaranteed the welfare of all within the framework of a universal obligation to the sovereign. The ruler ought to be a father to his people, his children; and power should be personal and direct, not institutionalized and mediated by land- or serf owner. Such a frame of mind may also account for the strong urge to take revenge on the nobles and officials, on their modern and evil way of life.[23]
Pugachev’s followers were particularly frightened by apparent economic and social changes. They wished to recapture the old ideals of service and community in a hierarchy ordained by God. They needed a palpable sense of direct relationship with the source of sovereign power. The Cossacks were most keenly aware of the loss of their special status and direct contact with the czar and his government.
The Imperial government endeavored to keep the matter of the rebellion strictly secret or, failing that, to portray it as a minor outbreak that would soon be quelled. The absence of an independent Russian press at the time, particularly in the provinces, meant that foreigners could read only what the government chose to print in the two official papers, or whatever news they could obtain from correspondents in the interior. (Alexander, 522) Russian government undertook to propagate in the foreign press its own version of events and directed its representatives abroad to play down the revolt.[24]
The Russian government favored the use of manifestos to communicate with the people of Russia. Catherine thought that exhortations to abandon him would excite popular antipathy for his cause and elicit divisions within rebel ranks. Her printed pronouncements were widely distributed in the turbulent areas; they were read on the public squares and from the parish pulpits. In the countryside local authorities were instructed to read them to gatherings of the people, who were then required to sign the decree. These government proclamations produced little positive effect. They actually added more confusion and even provoked unrest when the peasantry refused to believe or sign them.[25]
Much of the blame for the spread of the insurrection must be laid on the local authorities in Russia. “They were lax, timid, and indecisive; their countermeasures were belated, futile, and lost lives needlessly.”[26] Catherine herself recognized this assessment. As Catherine said “I consider the weak conduct of civil and military officials in various localities to be as injurious to the public welfare as Pugachev and the rabble he has collected.”[27] The weakness could not have been entirely the fault of the officials. The local bureaucracy in Russia was too remote and too inefficient to adequately deal with even the most basic administrative matters.
Pugachev’s success in holding out against suppression for over a year proved to be a powerful incentive for future reforms. It made apparent to the government several problems with their treatment of the provinces. They were left weakly controlled and consequently, susceptible to outbreaks of peasant violence. The most crucial lesson Catherine II drew from the Pugachev rebellion, was the need for a firmer military grasp on all parts of the Empire, not just the external frontiers. For instance, when the governor of the Kazan guberniya called for assistance against the approaching Pugachev, there was no force available to relieve him. The revolt did occur at a sensitive point in time for the Russian government because many of their soldiers and generals were already engaged in a difficult war on the southern borders with Ottoman Turkey. However, the professional army available outside the gates of Kazan to counter the Cossack-based army of Pugachev only consisted of 800 men.[11]
Media[edit]
- The Captain’s Daughter (1836 historical novel by Alexander Pushkin) Imperial officer Pyotr Grinyov is sent to a remote outpost. While traveling he is lost in a snowstorm, where he encounters a stranger who guides him to safety. He gratefully gives the stranger his fur coat and they part ways when the storm ends. Later his outpost is attacked by Pugachev’s forces, led by the stranger — who turns out to be Pugachev himself. Pugachev, impressed with the young man’s integrity, offers him a place in his army. The officer has to choose between loyalty to his commission or following the charismatic Pugachev.
- Tempest (1958 film) An adaptation of The Captain’s Daughter produced by Dino de Laurentis and directed by Alberto Lattuada. It starred Geoffrey Horne as Piotr Grinov, Silvana Mangano as Masha Miranov and Van Heflin as Emelyan Pugachov.
References[edit]
- ^ «Catherine the Great». Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f Tucker, Spencer C. (2017). The Roots and Consequences of Civil Wars and Revolutions: Conflicts that Changed World History. ABC-CLIO. p. 140. ISBN 9781440842948. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ (in Russian) К. Амиров. Казань: где эта улица, где этот дом, Казань, 1995., стр 214–220
- ^ Forster 1970, pp. 165-172.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 163.
- ^ a b Forster 1970, p. 169.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 195.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 197.
- ^ Pugachevshchina vol. 1 document 7, author’s translation from Russian.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 181.
- ^ a b c De Madariaga 1981, p. 250.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 176.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 179.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 190.
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 180.
- ^ Alexander 1970b, pp. 520–536.
- ^ Bodger 1991, p. 563.
- ^ Bodger 1991, p. 564.
- ^ Alexander 1973, p. 100.
- ^ Longley, David (2014-07-30). Longman Companion to Imperial Russia, 1689-1917. Routledge. p. 50. ISBN 978-1-317-88220-6.
- ^ Christine Hatt (2002). Catherine the Great. Evans Brothers. pp. 28–29. ISBN 9780237522452.
- ^ NUPI — Centre for Russian Studies Archived 2007-02-14 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Forster 1970, p. 198.
- ^ Alexander 1970b, p. 528.
- ^ Alexander 1969, p. 95.
- ^ Alexander 1969, p. 144.
- ^ Jones 1973, p. 207.
Sources[edit]
- Alexander, John T. (1969). Autocratic politics in a national crisis: the Imperial Russian government and Pugachev’s revolt, 1773-1775. Bloomington: Indiana University Press.
- Alexander, John T. (1970a). «Recent Soviet Historiography on the Pugachev Revolt: A Review Article». Canadian-American Slavic Studies. Brill Publishers. 4 (3): 602–617. doi:10.1163/221023970X00716. ISSN 2210-2396.
- Alexander, John T. (1970b). «Western Views of the Pugachev Rebellion». Slavonic and East European Review. Modern Humanities Research Association and University College London, School of Slavonic and East European Studies. 48 (113): 520–536. eISSN 2222-4327. ISSN 0037-6795.
- Alexander, John T. (1973). Emperor Of The Cossacks: Pugachev and the Frontier Jacquerie of 1773-1775. Lawrence, Kansas: Coronado Press.
- Avrich, Paul (1972). Russian Rebels, 1600-1800. New York: Schocken Books.
- Bodger, Alan (1988). «The Kazakhs and the Pugachev uprising in Russia, 1773-1775». Research Institute for Inner Asian Studies (RIFIAS). Bloomington: Indiana University (11).
- Bodger, Alan (1991). «Nationalities in History: Soviet Historiography and the Pugačëvščina». Jahrbücher für Geschichte Osteuropas. 39 (4).
- Commercio, Michele E. (2004). «The ‘Pugachev rebellion’ in the context of post‐Soviet Kazakh nationalization». Nationalities Papers. 32 (1): 87–113. doi:10.1080/0090599042000186205. ISSN 0090-5992. S2CID 154353007 – via ResearchGate.
- De Madariaga, Isabel (1981). Russia in the Age of Catherine the Great. New Haven: Yale University Press. pp. 239–255. ISBN 0-300-02515-7.
- Forster, Robert (1970). Preconditions of Revolution in Early Modern Europe. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press. ISBN 9780801811760.
- Jones, Robert Edward (1973). The Emancipation of the Russian Nobility, 1762-1785. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691052083.
- Kagan, Donald; Ozment, Steven; Turner, Frank (2002). The Western Heritage, Eighth Edition. New York, New York: Prentice Hall Publishing. Archived from the original on February 13, 2006.
- Longworth, Philip (1973). «The Pugachev Revolt: The Last Great Cossack-Peasant Rising». Journal of European Studies. SAGE Publications. 3 (1). doi:10.1177/004724417300300101. eISSN 1740-2379. ISSN 0047-2441. S2CID 162422918.
- Longworth, Philip (1975). «The Pretender Phenomenon in Eighteenth Century Russia». Past & Present. Oxford University Press. 66 (66): 61–84. doi:10.1093/past/66.1.61. eISSN 1477-464X. ISSN 0031-2746.
- Pushkin, Aleksandr Sergeevich (2000). The Complete Works of Alexander Pushkin: History of the Pugachev Rebellion. Downham Market: Milner & Company Ltd.
- Raeff, Marc (1970). «Pugachev’s rebellion». In Forster, Robert (ed.). Preconditions of Revolution in Early Modern Europe. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press. pp. 197 ff. ISBN 9780801811760.
- Raeff, Marc (2009). «Pushkin’s The History of Pugachev: Where Fact Meets the Zero-Degree of Fiction» (PDF). In Bethea, David M. (ed.). The Superstitious Muse: Thinking Russian Literature Mythopoetically. Boston: Academic Studies Press. pp. 301–322. doi:10.2307/j.ctt1zxsj7q.17. ISBN 9781934843178. JSTOR j.ctt1zxsj7q.17.
- Yaresh, Leo (1957). «The ‘Peasant Wars’ in Soviet Historiography». American Slavic and East European Review. 16 (3): 241–259. doi:10.2307/3001170. JSTOR 33001170.
In other languages[edit]
- Akademiia nauk SSSR [Academy of Sciences of the USSR] (1975). In-t istorii SSSR [History of the USSR] (in Russian). Moscow: Tsentralʹnyi gosudarstvennyi arkhiv drevnikh aktov SSSR [Central government archive of ancient acts of the USSR].
- Pugachevshchina [Dark Deeds of Pugachev] (in Russian). Moscow: Gosizdat. [1926-1931]
- Palmer, Elena (2005). Peter III — Der Prinz von Holstein (in German). Erfurt, Germany: Sutton Publishing. ISBN 978-3-89702-788-6.
External links[edit]
- World History at KMLA
- Stavropol and Pugachyov’s rebellion
Крестьянская война под предводительством Е.И.Пугачёва 1773–1775 годов (Пугачёвщина, Пугачёвское восстание, Пугачёвский бунт) — третья в России крестьянская война против феодально-крепостнического гнёта. Охватила огромную территорию: Оренбургский край, Урал, Приуралье, Западная Сибирь, Среднее и Нижнее Поволжье. Вовлекла в движение до 100 тысяч активных повстанцев — русских крестьян, трудовые слои казачества и нерусских народностей, — открыто выявив антагонистические классовые отношения в условиях дальнейшего развития и упрочения новых капиталистических отношений в недрах старого феодального строя.
Обстановка в стране накануне
Классовая борьба накануне крестьянской войны принимала самые различные формы социального протеста, которые, однако, не затрагивали основ существуюшего строя. Только в крестьянской войне народ стихийно поднялся на борьбу за свои общенациональные классовые интересы: за свержение феодальной системы, но при сохранении прежней, искони привычной формы государственноё власти в виде монархии во главе с «хорошим мужицким царём».
Накануне крестьянской войны крупные восстания охватили до 250 тысяч помещичьих, монастырских и горнозаводских крестьян. Волнения затронули калмыков, башкир и другие народности Заволжского края. В сентябре 1771 года вспыхнуло восстание городских низов в Москве. Многолетние волнения трудового казачества Яицкого войска привели в январе 1772 года к восстанию против старшинской верхушки. В 1772 году происходили волнения среди казаков волжских и донских станиц. Правительство Екатерины II с большим трудом удерживало народ в повиновении. Война с Турцией 1768–74 годов и события в Польше ещё больше осложнили обстановку в стране, вызвали недовольство народа новыми тяготами.
Начало восстания
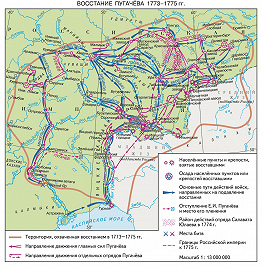
Крестьянская война началась в сентябре 1773 года в заволжских степях новым восстанием яицких казаков, во главе которых встал донской казак Емельян Иванович Пугачев. Ещё в августе 1773 года он собрал на хуторах под Яицким городком надёжных сторонников из казаков, усматривая при этом главную социальную силу движения не в казачестве, а в крепостном крестьянстве. Пугачев принял имя императора Петра III, что объективно соответствовало наивно-монархическим иллюзиям, жившим в народе. К середине сентября 1773 года приготовления к восстанию были закончены. Пугачев собрал первый повстанческий отряд из 80 казаков. 17 сентября он обнародовал манифест, которым пожаловал казаков, татар и калмыков, служивших в Яицком войске, старинными казачьими вольностями и привилегиями. 19 сентября повстанцы подступили к Яицкому городку, но, не имея артиллерии, отказались от штурма крепости. Отсюда Пугачев предпринял поход к Оренбургу, пополняя отряд казаками, солдатами, татарами, калмыками, казахами и помещичьими крестьянами, захватывая пушки, оружие и боеприпасы. 5 октября повстанцы блокировали Оренбург, имея до 2,5 тысяч бойцов при 20 пушках, и держали его в осаде около 6 месяцев.
Осада Оренбурга и первые военные успехи
Слухи о боевых успехах повстанцев вызвали стихийные волнения среди помещичьих и горнозаводских крестьян и нерусского населения Оренбургской губернии. Пугачёв приступил к планомерной организации восстания, распространяя его на новые районы. Из Бердской слободы по селениям и заводам рассылались посланцы с манифестами Пугачёва, который объявлял народу вечную волю, освобождал от подневольного труда на помещиков и заводчиков, от податей и повинностей, жаловал землю, призывал к истреблению крепостников, провозглашал свободу для любых вероисповеданий. Под власть повстанческого центра перешла значительная часть Оренбургской губернии. В лагерь восставших шли тысячи добровольцев. Крестьяне везли продовольствие и фураж, с уральских заводов доставлялись пушки, оружие, боеприпасы.
К началу декабря 1773 года в отрядах Пугачёва под Оренбургом находилось до 25 тысяч бойцов с 86 пушками. Для управления войском Пугачёв создал Военную коллегию, которая одновременно являлась админстративно-политическим центром восстания. Правительство организовало карательный отряд во главе с генералом Каром. В начале ноября он выступил на помощь осаждённому Оренбургу, но в сражении 7-9 ноября под деревней Юзеевой был разгромлен. В ноябре были разбиты и другие карательные отряды, следовавшие к Оренбургу из Симбирска и Сибири. В ноябре 1773 года — начале января 1774 года восстание охватило Южный Урал, значительную часть Казанской губернии, Западную Сибирь, Западный Казахстан. Восстал народ Башкирии во главе с Кинзей Арслановым, Салаватом Юлаевым. Образовались крупные очаги повстанческого движения под Уфой — И.Чика-Зарубин, Екатеринбургом — И.Белобородов, Челябинском — И. Грязнов, Самарой — И.Арапов, Заинском — В.Торнов, Кунгуром и Красноуфимском — И.Кузнецов, Салават Юлаев, Яицким городком — М.Толкачев). Отсутствие единого стратегического плана, слабая связь с отдалёнными районами восстания привели к тому, что Военная коллегия не смогла возглавить движение по всей территории. Занятый осадой Оренбурга и Яицкого городка, Пугачёв отказался от похода в Поволжье, которое было готово к восстанию. Это ограничило стратегическую базу крестьянской войны, позволило правительству выиграть время и собрать воинские силы.
Военные поражения и расширение района Крестьянской войны
В декабре 1773 года к районам восстания были отправлены несколько кавалерийских и пехотных полков во главе с генералом А.И.Бибиковым, которые повели наступление и нанесли ряд поражений повстанцам под Самарой, Кунгуром, Бузулуком. Пугачёв не смог оказать помощи своим авангардным отрядам, которые вели неравную борьбу и отступали по всему фронту. Лишь после падения Бузулука он вывел часть сил из-под Оренбурга и попытался остановить дальнейшее продвижение неприятеля. Для генерального сражения Пугачев избрал сильно укреплённую Татищеву крепость. В битве 22 марта повстанцы были разгромлены, потеряли всю артиллерию и понесли крупные потери. 24 марта корпус подполковника Михельсона нанёс поражение повстанцам под Уфой, а вскоре захватил в плен и их атамана И. Чику-Зарубина. Сняв осаду Оренбурга, Пугачев отступил к Каргале, где 1 апреля дал новое сражение карательным войскам, но, понеся крупные потери, лишившись видных помощников, захваченных в плен (М.Шигаев, Т.Подуров, А.Витошнов, М.Горшков, И.Почиталин), укрылся в Уральских горах.
Крупные очаги восстания к середине апреля 1774 года были разгромлены, но отдельные отряды активно действовали в Закамском крае, в Башкирии (Салават Юлаев), на заводах Южного Урала (Белобородов), в Оренбургских степях (Овчинников). Пугачёв вел деятельную организацию нового повстанческого войска, своими воззваниями поднял на восстание всю Башкирию, заводской Урал. Собрав 5 тысяч бойцов, Пугачёв 6 мая захватил Магнитную крепость (6 мая) и соединился здесь с отрядами Белобородова и Овчинникова. Продвигаясь вверх по Яику, он взял штурмом Троицкую крепость), но 20 мая был разгромлен и снова ушёл в Уральские горы. Корпус Михельсона, преследуя Пугачева, нанёс ему ряд поражений, но Пугачев, умело используя тактику партизанской борьбы, каждый раз уходил от преследования и сберегал главные силы от окончательного разгрома, а потом снова собирал многотысячные отряды. Вытесненный к середине июня 1774 года из районов заводского Урала, Пугачев решил вывести свои отряды к Казани, взять её и предпринять давно задуманный поход на Москву. 12 июля повстанческие отряды штурмовали Казань, овладели предместьями и городом, но не смогли взять крепости, где засели остатки гарнизона, и были разгромлены подоспевшим корпусом Михельсона. Новое сражение за Казань произошло 15 июля. Потеряв всю артиллерию, до 2 тысяч убитыми и 5 тысяч пленными, Пугачёв отошёл на север и переправился на правый берег Волги у Сундыря.
Поражение восстания
Появление повстанцев на правобережье Волги вызвало всеобщее крестьянское восстание, поддержанное нерусскими народностями Поволжья. 18 июля Пугачёв обнародовал манифест об освобождении крестьян от крепостной неволи, о безвозмездной передаче земли народу, о повсеместном истреблении дворян. Силы восставших росли. В Поволжье, кроме главной повстанческой армии, действовали многочисленные крестьянские отряды, насчитывавшие сотни и тысячи бойцов. Движение охватило большинство поволжских уездов, подошло к границам Московской губернии, реально угрожало Москве, где волновались городские низы, фабричные и барские люди. Сложились реальные условия для похода повстанческой армии на Москву, опираясь на многочисленные очаги крестьянского движения. Но Пугачёв допустил стратегическую ошибку, покинув районы наибольшего размаха крестьянского движения, и устремился с главными силами на юг, к Дону, где надеялся пополнить отряды донскими казаками и лишь тогда предпринять поход на Москву. Отряды Пугачёва, продвигаясь на юг, повсюду встречали поддержку простого народа. 20 июля повстанцы взяли Курмыш, 23 июля — Алатырь, 27 июля — Саранск, 2 августа — Пензу, 4 августа — Петровск, 6 августа — Саратов. Собирая добровольцев из крестьян, горожан и казаков, Пугачёв уходил всё дальше на юг, оставляя за собой десятки локальных, разрозненных повстанческих отрядов.
Ошибочный стратегический замысел Пугачёва позволил карателям по частям разгромить крестьянское движение в Среднем Поволжье, оттеснить главные повстанческие силы на юг — в малонаселённые районы Нижнего Поволжья. В августе 1774 года Екатерина II собрала для борьбы с повстанцами огромную армию: до 20 пехотных и кавалерийских полков, казачьи части и дворянские корпуса. Войску Пугачёва удалось взять Дмитриевск (Камышин) и Дубовку, увлечь за собой калмыков, но попытка взять Царицын штурмом не удалась. Здесь Пугачёва покинули многие донские казаки, ушли калмыки. Преследуемый корпусом Михельсона, Пугачёв отступил к Черному Яру, потеряв надежду поднять донское казачество на восстание. 25 августа у Солениковой ватаги произошло последнее крупное сражение. Из-за предательства группы заговорщиков — яицких казачьих старшин — повстанцы в начале боя лишились артиллерии. Пугачёв был разгромлен, бежал в заволжские степи, но вскоре был арестован и 15 сентября доставлен в Яицкий городок.
Следствие над Пугачёвым производилось в Яицком городке, Симбирске и в Москве, куда доставили и других видных деятелей Крестьянской войны. По приговору суда 10 января 1775 года в Москве на Болотной площади были казнены Пугачёв, Перфильев, Шигаев, Подуров и Торнов; остальные обвинённые подверглись телесным наказаниям и были сосланы на каторжные работы. В феврале 1775 года в Уфе был казнён Чика-Зарубин. Крестьянская война не закончилась после разгрома главного повстанческого войска. До ноября 1774 года в Башкирии активно действовали отряды Салавата Юлаева. Продолжали бороться крестьяне Среднего Поволжья и Центральной губерний. Движение в Нижнем Поволжье было подавлено только к лету 1775 года. Массовые репрессии против населения Поволжского края и Оренбургской губернии продолжались до середины 1775 года.
Причины поражения и итоги Крестьянской войны под предводительством Емельяна Пугачёва
Крестьянская война 1773–1775 годов потерпела поражение, неизбежное для любого стихийного выступления крестьянства в эпоху феодализма. Причины поражения Крестьянской войны коренились в стихийности и разрозненности движения, в отсутствии ясно осознанной программы борьбы. Пугачёв и его Военная коллегия не смогли организовать армию для успешной борьбы с правительствельными войсками. Стихийному выступлению народа господствующий класс и государство противопоставили регулярную армию, административный и полицейский аппарат, финансы, церковь. Народ потерпел тяжёлое поражение, но приобрёл опыт революционной борьбы. Крестьянская война поколебала веру народа в незыблемость феодальных порядков, ускорила крушение крепостничества. Последующее развитие классовой борьбы русского крестьянства в XVIII–XIX веках шло под воздействием примера Крестьянской войны. Страх перед новой крестьянской войной вынудил царизм в 1861 году пойти на проведение крестьянской реформы 1861 года.
Помощь в написании учебных работ
ПУГАЧЁВА ВОССТА́НИЕ 1773–75 (Крестьянская война, Пугачёвский бунт, Пугачёвщина), антиправительственное выступление в Рос. империи. Вызвано недовольством яицких казаков, окончательно утративших к 1770-м гг. свои привилегии, усилением повинностей, распространением помещичьего землевладения и потерей земли башк. населением, увеличением масштаба рекрутской повинности в связи с рус.-тур. войной 1768–74, сопротивлением христианизации поволжских народов. Казаки неоднократно бунтовали, последний раз в 1772.
Предводитель – Е. И. Пугачёв [действовал совм. с так называемыми Тайным советом (Секретной думой) и Воен. коллегией]. 17(28).9.1773 он якобы от имени имп. Петра III в Бударинском форпосте (ныне с. Бударино Акжаикского р-на Западно-Казахстанской обл., Казахстан) обнародовал «указ», в котором объявил о пожаловании старинными казачьими вольностями и привилегиями яицких казаков, а также татар и калмыков, служивших в Яицком войске. В дальнейшем всем участникам восстания обещал «вечную вольность, реки, леса, все выгоды … чины и честь» и др.
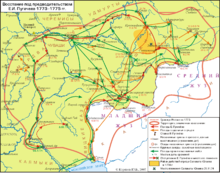
П. в. охватило Оренбургскую, Казанскую, Нижегородскую, Астраханскую и Сибирскую губернии. В нём участвовало св. 100 тыс. чел. – помимо яицких и оренбургских казаков, также горнозаводские и частновладельческие крестьяне, башкиры, мишари и др. поволжские народы. Воен. силы состояли из Гл. повстанческого войска (до 25 тыс. чел.) во главе с Пугачёвым и ряда мобильных вооруж. формирований [каждое по неск. тысяч чел.; возглавлялись Салаватом Юлаевым, казаком И. Н. Зарубиным (Чикой), отставным капралом И. Н. Белобородовым и др.]. Везде, где побеждали восставшие, Пугачёв оставлял отд. отряды, назначал «главных командиров», казнил сохранявших верность имп. Екатерине II офицеров (часто с членами их семей) и казаков, священнослужителей и др. лиц.
В окт. 1773 Гл. повстанческое войско осадило Оренбург, в ноябре разгромило двигавшиеся на помощь осаждённому городу авангард экспедиционного корпуса (ок. 1,7 тыс. чел.) под команд. ген.-м. В. А. Кара и отряд (1,2 тыс. чел.) полк. П. М. Чернышёва. В кон. 1773 – нач. 1774 мобильные отряды восставших овладели Осой, Самарой, Ставрополем (ныне Тольятти), Красноуфимском, блокировали Уфу, Мензелинск, Кунгур и др. В 1774 войска под команд. ген.-аншефа А. И. Бибикова (св. 6 тыс. чел.), направленные на подавление П. в., нанесли ряд поражений повстанцам, в частности 22 марта (2 апр.) близ Татищевой крепости (ныне с. Татищево Переволоцкого р-на Оренбургской обл.; на следующий день восставшими была снята осада Оренбурга), 24 марта (4 апр.) близ Уфы и 1(12) апр. близ Сакмарского городка, около Оренбурга. В плен были взяты видные соратники Пугачёва, в т. ч. И. Н. Зарубин (Чика), И. Я. Почиталин, М. Д. Горшков, М. Г. Шигаев. Однако собранное вскоре Пугачёвым новое войско в мае заняло Магнитную (ныне Магнитогорск), Карагайскую, Троицкую (ныне Троицк) и др. крепости. В мае/июне – июне деташемент (отряд) под команд. подполк. И. И. Михельсона вытеснил осн. силы Пугачёва из Оренбургской губ. в Казанскую. 12(23) июля восставшие штурмовали Казань, заняли б. ч. города (кроме кремля, где находился гор. гарнизон), но вечером того же дня и затем 15(26) июля были разбиты Михельсоном. Лишившись артиллерии и понеся значит. потери, Пугачёв и его сторонники (ок. 500 чел.), которые рассчитывали на поддержку донских казаков, направились на юг по Волге. На их сторону с 20(31) июля до 17(28) авг. перешло население Курмыша (ныне село Пильнинского р-на Нижегородской обл.), Алатыря, Саранска, Пензы, Петровска, Дмитриевска (ныне Камышин), Дубовки; Саратов был взят с боем. «Именными указами» [от 28 июля (8 авг.) и 31 июля (11 авг.)] Пугачёв объявлял об отмене крепостного права, рекрутской повинности, подушной подати и всех налогов, о наделении крестьян землёй и угодьями «без покупки и без оброку», разрешал креститься двумя перстами. В Нижегородской, Казанской и Астраханской губерниях вспыхнули многочисл. крестьянские мятежи. 21 авг. (1 сент.) участники П. в. неудачно штурмовали Царицын, а 25 авг. (5 сент.) их 10-тысячное войско было разгромлено полк. И. И. Михельсоном в сражении близ Солениковой ватаги (ныне близ с. Солодники Черноярского р-на Астраханской обл.). С небольшим отрядом Пугачёв бежал. В сентябре своими быв. сторонниками сдан властям и доставлен в Яицкий городок. Однако восстание продолжилось в Оренбургской губ. (отряды Базаргула Юнаева, Юламана Кушаева и Салавата Юлаева ликвидированы к кон. 1774). К лету 1775 оно окончательно подавлено силами частей рос. армии во главе с гр. П. И. Паниным, переброшенных с Дунайского фронта после окончания рус.-тур. войны 1768–74.
В 1774–75 под следствием находилось св. 10 тыс. чел., из них ок. 1,1 тыс. чел. подвергнуты разл. наказаниям, в т. ч. 34 казнены, 178 сосланы на каторгу, 86 определены в солдаты. Указом Сената от 15(26).1.1775 р. Яик переименована в р. Урал, Яицкий городок – в Уральск, Верхнеяицкая крепость – в Верхнеуральскую (ныне Верхнеуральск), а Яицкое казачье войско – в Уральское.
| Восстание Пугачёва | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Суд Пугачёва |
||||||
|
||||||
| Противники | ||||||
| Яицкие казаки
Башкиры Татары Крестьяне Горнозаводские Рабочие Мишары Казахи |
||||||
| Командующие | ||||||
| Емельян Пугачёв
Андрей Овчинников Салават Юлаев Юлай Азналин Кинзя Арсланов Канзафар Усаев |
Василий Кар
Александр Бибиков Пётр Панин Иван Михельсон |
Крестьянская война 1773—1775 годов под предводительством Емельяна Пугачёва (Пугачёвщина, Пугачёвское восстание, Пугачёвский бунт) — восстание (бунт) яицких казаков, переросшее в полномасштабную крестьянскую войну под предводительством Е. И. Пугачёва .
Начало восстания[]
В России при Екатерине II усилился госудасртвенный и крепостнический гнёт. Было принято несколько указов, которые увеличивали власть помещиков над крепостными. Помещики теперь могли ссылать своих крестьян на каторжные работы. Крестьянам же запрещалось подавать жалобы на своих хозяев. Всё меньше оставалось места для вольных людей. Власти вели наступление на окраины страны, издавна укрывавшие беглых со всей России. Жесткая сословная структура общества лишала низы последних прав. В ответ на это – самое мощное из народных волнений.
Его возглавил донской казак Емельян Иванович Пугачёв. Это движение переросло в настоящую войну и представляло огромную опасность для власти.
Восстание зародилось на реке Яик, в области Яицкого казачьего войска. Там и появился Пугачёв. Крепкий широкоплечий человек с чёрной окладистой бородой предстал перед казаками и объявил себя… императором Петром III.
Образ погибшего императора в народе приобрёл мифические черты. Шла молва, что государь думал дать крестьянам «волю» и за это его убили.
Яицкие казаки в походе
Пугачёв поднял огромные маччы людей. Сказывались его казачья закалка, знание жизни, военный опыт. Далеко не все верили, что Пугачёв тот, за кого мебя выдаёт. Но народ шёл за атаманом, видя в нём своего избавителя. Так неграмотный казак перевоплотился в Петра Фёдоровича.
В сентябре 1774 года Пугачёв с отрядом из 80 человек пошёл на столицу казачьего войска – Яицкий городок. Весть о появившемся «императоре» мгновенно разнеслась по округе. К нему присоединились отряды татар, башкир и калмыков. Войско самозванца росло с каждым днём. Своими «манифестами» Пугачёв жаловал казаков землями и лугами, рыбными ловлями и деньгами, свинцом и порохом и «всею вольностью». Нерусским народам он гарантировал незыблемость прежних устоев и прав, а старообрядцам обещал свободу исповедания.
Пугачёв в тюрьме
Повстанцы не решились штурмовать Яицкий городок. Вместо этого они захватывали одну за другой небольшие крепости на степных рубежах страны. Гарнизоны здесь были небольшими. Как правило, солдаты переходили на сторону восставших. Сопротивлявшихся пугачёвцы убивали. Всё это прекрасно показано Александром Пушкиным в его повести «Капитанская дочка»
Несколько десятков тысяч человек Пугачёв привёл к Оренбургу и начал осаду города.
От Оренбурга до Казани[]
Осада затянулась, а воинство Пугачёва достигло уже 30–40 тысяч человек. Пугачёв окружил себя «гвардией» и щедро раздавал сподвижникам чины и титулы. Вооружения не хватало. Ружья и сабли имелись лишь у казаков. Крестьянская масса довольствовалась топорами, вилами и рогатинами. Прибывали к Пугачёву и приписные крестьяне на Урале и в Башкирии. С уральских заводов доставилии под Оренбург пушки.
Александр Бибиков
Правительство обеспокоилось разраставшимся мятежом. К Оренбургу направился отряд генерал-майора В.А. Кара. Вместе с ним шли и башкирские части под командованием Салавата Юлаева. Повстанцы разгромили генерала, а Салават Юлаев со своими частями перешел на сторону Пугачёва.
Между тем на выручку Оренбургу двигалось новая правительственная армия. Командовал ею генерал А.И. Бибиков. Его отряды в нескольх сражениях разгромили пугачёвских сподвижников. У самозванца осталось лишь 500 человек. С ними он отступил в район уральских заводов. Правительство поспешило объявить о ликвидации мятежа.
Но Пугачёв не отступил, и не сдался. Он захватил несколько заводов получил новое вооружение и с 8-тысячным войском направился к Волге. Армия восставших вновь превратилась в грозную силу. Подойдя к Казани, они насчитывали вновь около 20 тысяч человек.
В сентябре 1773 г. в Заволжье вспыхнуло новое восстание яицких казаков. Его возглавил донской казак Е.И. Пугачев, принявшим имя императора Петра III. 17 сентября он обнародовал манифест, которым пожаловал Яицкое войско старинными вольностями и привилегиями. 18 сентября его отряд из 80 казаков подступил к Яицкому городку, но из-за отсутствия артиллерии отказался от штурма. Отсюда Пугачев предпринял поход к Оренбургу. В пути отряд пополнился казаками, солдатами, татарами, калмыками, крестьянами, работными людьми. В сдавшихся Пугачеву верхне-яицких крепостях были захвачены пушки, оружие и боеприпасы. 5 октября повстанцы блокировали Оренбург, имея до 2,5 тыс. бойцов при 20 пушках, и держали его в осаде около 6 месяцев.
Из Бердской слободы (ставка Пугачева близ Оренбурга) рассылались посланцы с манифестами Пугачева. В них он объявлял народу вечную волю, освобождение от труда на помещиков, заводчиков, от податей и повинностей, жаловал землю, провозглашал свободу вероисповедания. К началу декабря 1773 г. в повстанческих отрядах под Оренбургом находилось до 25 тыс. бойцов и 86 пушек. Для управления войсками Пугачев создал Военную коллегию.
Попытки деблокировать Оренбург в ноябре 1773 г. провалилась. В сражении 7–9 ноября под Юзеевой направленный к крепости отряд генерала В.А. Кара (3,5 тыс. чел., 10 пушек) был разбит. Потерпели поражение и другие отряды, шедшие к Оренбургу. В ноябре 1773 — начале января 1774 г. восстание охватило Южный Урал, Башкирию, часть Казанской губернии, где действовали отряды сподвижников Пугачева. Однако стойкая оборона Оренбурга позволила правительству выиграть время и собрать воинские силы. В декабре 1773 г. к районам восстания был отправлен корпус во главе с генералом Бибиковым (6,5 тыс. чел., 30 пушек), разбивший повстанцев под Самарой, Кунгуром, Бузулуком. 22 марта в генеральном сражении у Татищевой крепости (близ Оренбурга) Пугачев потерпел поражение от войск под командованием генерала Голицына. Сняв осаду Оренбурга, Пугачев отошел к Сакмарскому городку, где 1 апреля дал новое сражение Голицыну, но потерпел поражение и укрылся в Уральских горах.
Там он деятельно подготовил новое войско, используя сохранившиеся очаги восстания в Башкирии и на заводском Урале. Собрав до 5 тыс. бойцов, он захватил Магнитную крепость (6 мая) и соединился здесь с отрядами Белобородова и Овчинникова. 19 мая он взял штурмом Троицкую крепость, но 20 мая был разгромлен. Пугачев снова ушел в Уральские горы, где его настиг отряд подполковника Михельсона. Вытесненный к середине июня 1774 г. из районов заводского Урала, Пугачев вывел свои отряды к Казани. 12 июля они штурмовали Казань, овладели предместьями и городом, но не смогли взять крепости. Решающее сражение за Казань между повстанцами и отрядом Михельсона произошло 15 июля. В нем Пугачев потерял всю артиллерию, до 2 тыс. убитыми и 5 тыс. пленными. Он отошел к северу и переправился на правый берег Волги.
Появление повстанцев на правобережье вызвало здесь общее крестьянское восстание. В июле Пугачев обнародовал манифест об освобождении крестьян от крепостной неволи, о безвозмездной передаче земли народу, о повсеместном истреблении дворян. Восстание охватило большинство поволжских уездов. Однако Пугачев покинул районы наибольшего размаха движения и устремился с главными силами на юг, к Дону, где надеялся пополнить отряды донскими казаками, а, возможно, и наладить взаимодействие с турецкой армией на Северном Кавказе.23 июля повстанцы взяли Алатырь, 27 июля — Саранск, 2 августа — Пензу, 6 августа — Саратов. Отход их главных сил позволил царским войскам разгромить крестьянское движение по частям и оттеснить Пугачева в малонаселенные районы Нижнего Поволжья. 11 августа у Дмитриевска Пугачев разбил отряд майора Дица (1,5 тыс. чел.) Это сражение стало последней победой Пугачева, после которой он сумел овладеть Дмитриевском и Дубовкой. Однако попытка взять 21 августа Царицын не удалась. После этой неудачи Пугачева покинуло большинство донских казаков и калмыки. Пугачев отступил к Черному Яру. Настигнув здесь его армию, Михельсон отрезал ей путь к отходу в южном направлении. Тогда Пугачев атаковал Михельсона у Солениковой ватаги, но потерпел жестокое поражение. Повстанцы потеряли 2 тыс. чел. убитыми и 6 тыс. пленными. Эта битва решила судьбу восстания. С двумя сотнями приближенных Пугачев бежал за Волгу. Там его вскоре (8 сентября) схватили ближайшие сподвижники и выдали царским властям. Пугачева привезли в Москву и в начале 1775 г. казнили.
После ликвидации пугачевской армии восстания длились еще почти год. С. Юлаев действовал в Башкирии до ноября 1774 г. Продолжались выступления крестьян Среднего Поволжья и центральных губерний. Движение в Нижнем Поволжье было подавлено только к лету 1775 г.