Последнее обновление: 03.03.2021
-
Глава 1. MS SQL Server в .NET 6
-
Строка подключения для MS SQL Server
-
Подключение к MS SQL Server
-
Пул подключений
-
Выполнение команд и SqlCommand
-
Чтение результатов запроса и SqlDataReader
-
Типизация результатов SqlDataReader. Сопоставление типов C# и SQL
-
Получение скалярных значений
-
Параметризация запросов
-
Выходные параметры запросов
-
Добавление и выполнение хранимых процедур
-
Выходные параметры хранимых процедур
-
Транзакции
-
Сохранение и извлечение файлов из базы данных
-
-
Глава 2. DataSet
-
SqlDataAdapter и загрузка данных в DataSet
-
Работа с DataSet без базы данных
-
Сохранение изменений DataSet в базе данных
-
-
Глава 3. SQLite в C# и .NET
-
Подключение к базе данных SQLite
-
Выполнение запросов к БД SQLite и SqliteCommand
-
Чтение результатов запроса и SqliteDataReader
-
Сопоставление типов C# и SQLite. Типизация SqliteDataReader
-
Параметризация запросов к БД Sqlite
-
Получение скалярных значений в SQLite
-
Сохранение и извлечение файлов из базы данных SQLite
-
- Глава 1. MS SQL Server в .NET 5
- Строка подключения для MS SQL Server
- Подключение к MS SQL Server
- Пул подключений
- Выполнение команд и SqlCommand
- Чтение результатов запроса и SqlDataReader
- Типизация результатов SqlDataReader. Сопоставление типов C# и SQL
- Получение скалярных значений
- Параметризация запросов
- Выходные параметры запросов
- Добавление и выполнение хранимых процедур
- Выходные параметры хранимых процедур
- Транзакции
- Сохранение и извлечение файлов из базы данных
- Глава 2. DataSet
- SqlDataAdapter и загрузка данных в DataSet
- Работа с DataSet без базы данных
- Сохранение изменений DataSet в базе данных
- Глава 3. SQLite в C# и .NET
- Подключение к базе данных SQLite
- Выполнение запросов к БД SQLite и SqliteCommand
- Чтение результатов запроса и SqliteDataReader
- Сопоставление типов C# и SQLite. Типизация SqliteDataReader
- Параметризация запросов к БД Sqlite
- Получение скалярных значений в SQLite
- Сохранение и извлечение файлов из базы данных SQLite
Помощь сайту
YooMoney:
410011174743222
Перевод на карту
Номер карты:
4048415020898850
Введение
ADO.NET – это набор классов (фреймворк) для работы с базами данных, а также XML файлами. Аббревиатура ADO расшифровывается как ActiveX Data Objects. Данная технология имеет методы и классы для извлечения и обработки данных.
Список .NET приложений, которые используют возможности ADO.NET для различных действий с БД:
-
ASP.NET Web Applications
-
Console Applications
-
Windows Applications.
Структуры подсоединения к БД
Можно определить два типа архитектуры подключения:
- Архитектура, подключенная к базе: подсоединена к БД на протяжении всего рабочего времени.
- Архитектура, не подсоединённая к БД: приложение, автоматически подключается/отключается в процессе работы. Приложения на такой архитектуре используют временные данные, хранящиеся на стороне клиента (DataSet).
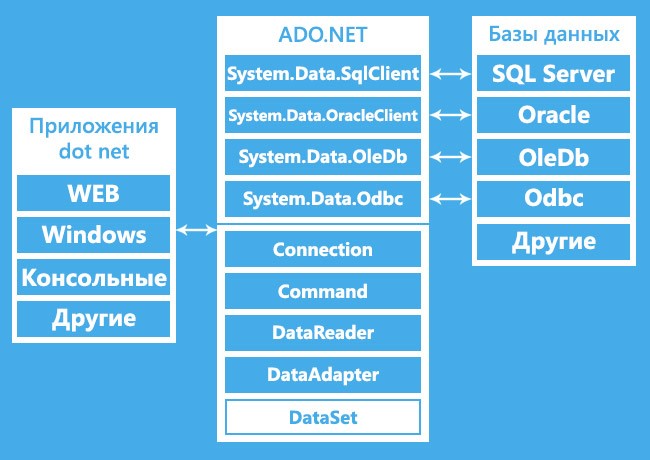
ADO.NET и его библиотеки классов
На данной диаграмме видны различные типы приложений (Веб приложения, консольные приложения, приложения для Windows и так далее), использующие ADO.NET для подсоединения к БД (SQL Server, Oracle, OleDb, ODBC, XML-файлы и так далее).
Классы в ADO.NET
Также на предыдущем рисунке мы видим различные классы, а именно:
- Connection Class
- Command Class
- DataReader Class
- DataAdaptor Class
- DataSet.Class
1. Connection Class
Данные классы применяются в ADO.NET для подсоединения к БД.
2. Command Class
Данный класс обеспечивает хранение и выполнение SQL команд. Ниже приведены различные команды, выполняющиеся с помощью данного класса.
- ExecuteReader: Возвращает данные к клиенту в виде строк.
- ExecuteNonQuery: Выполняет команду, изменяющую данные в базе данных.
- ExecuteScalar: Данный класс возвращает только одно значение.
- ExecuteXMLReader: (Только для классов SqlClient) Получает данные из базы данных SQL Server 2000 с помощью XML-потока.
3. DataReader Class
DataReader используется для получения данных. Он используется в сочетании с Command Class для выполнения SQL-запроса.
5. DataSet Class
Класс DataSet – сердце ADO.NET, представляющее из себя набор объектов DataTable. Каждый такой объект содержит много объектов DataColumn и DataRow.
Подключение ADO.NET к базе данных
Для настройки подключения Вы должны быть знакомы со строками подключения (connection strings). ConnectionString – строка переменной (регистр не учитывается). Строки подключения нужны нам для параметра SQLConnection. Данные примеры содержат основные значения, а именно: provider, server, database, userid и password.
SQL Аутентификация
String constr=«server=.;database=institute;user id=rakesh;password=abc@123»;
Или:
String constr=«data source=.;initial catalog=institute;uid=rakesh;pwd=abc@213»;
Windows Аутентификация (Windows Authentication)
String constr=«server=.;database=institute;trusted_connection=true»
Или:
String constr=«server=.;initial catalog=institute;integrated security=true»
Видео курсы по схожей тематике:
Получение и отображение данных из базы данных
Получить и отобразить данные можно по такой схеме:
- Создайте объект SqlConnection, используя строку подключения.
- Откройте соединение.
- Создайте SQLCommand. Укажите тип SQLCommand.
- Выполните команду (используйте executereader).
- Получить результат (используйте SqlDataReader).
- Закройте соединение.
- Получите результат.
Ниже приведен код для подсоединения к SQL:
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Data.OracleClient;
using System.Data.OleDb;
using System.Data.Odbc;
namespace AdoDemo
{
public partial class WebForml : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(«data source=.; database=Sample; integrated security=SSPI»);
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(«Select * from tblProduct», con);
con.Open();
SqlDataReader rdr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
GridView1.DataSource = rdr;
GridView1.DataBind();
con.Close();
}
}
}
Вы должны использовать System.Data.SqlClient для подключения к SQL. В предыдущем коде мы использовали классы SqlConnection, SqlCommand и SqlDataReader, потому что наше приложение обращалось к SQL Server, а он понимает только SQL.
Бесплатные вебинары по схожей тематике:
Подключение к базе данных Oracle
При подключении к БД Oracle Вам нужно изменить имя некоторых классов, а именно SqlConnection на OracleConnection, SqlCommand на OracleCommand и SqlDataReader на OracleDataReader. Также вначале используйте System.Data.OracleClient.
Источник: http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/18fc30/understanding-the-basics-of-ado-net/
ADO.NET
ADO.NET is a set of classes (a framework) to interact with data sources such as databases and XML files. ADO is the acronym for ActiveX Data Objects. It allows us to connect to underlying data or databases. It has classes and methods to retrieve and manipulate data.
The following are a few of the .NET applications that use ADO.NET to connect to a database, execute commands and retrieve data from the database.
- ASP.NET Web Applications
- Console Applications
- Windows Applications.
Various Connection Architectures
There are the following two types of connection architectures:
- Connected architecture: the application remains connected with the database throughout the processing.
- Disconnected architecture: the application automatically connects/disconnects during the processing. The application uses temporary data on the application side called a DataSet.
Understanding ADO.NET and it’s class library

In this diagram, we can see that there are various types of applications (Web Application, Console Application, Windows Application and so on) that use ADO.NET to connect to databases (SQL Server, Oracle, OleDb, ODBC, XML files and so on).
Important Classes in ADO.NET
We can also observe various classes in the preceding diagram. They are:
- Connection Class
- Command Class
- DataReader Class
- DataAdaptor Class
- DataSet.Class
1. Connection Class
In ADO.NET, we use these connection classes to connect to the database. These connection classes also manage transactions and connection pooling. To learn more about connection classes, start here: Connection in ADO.NET.
2. Command Class
The Command class provides methods for storing and executing SQL statements and Stored Procedures. The following are the various commands that are executed by the Command Class.
- ExecuteReader: Returns data to the client as rows. This would typically be an SQL select statement or a Stored Procedure that contains one or more select statements. This method returns a DataReader object that can be used to fill a DataTable object or used directly for printing reports and so forth.
- ExecuteNonQuery: Executes a command that changes the data in the database, such as an update, delete, or insert statement, or a Stored Procedure that contains one or more of these statements. This method returns an integer that is the number of rows affected by the query.
- ExecuteScalar: This method only returns a single value. This kind of query returns a count of rows or a calculated value.
- ExecuteXMLReader: (SqlClient classes only) Obtains data from an SQL Server 2000 database using an XML stream. Returns an XML Reader object.
3. DataReader Class
The DataReader is used to retrieve data. It is used in conjunction with the Command class to execute an SQL Select statement and then access the returned rows. Learn more here: Data Reader in C#.
4. DataAdapter Class
The DataAdapter is used to connect DataSets to databases. The DataAdapter is most useful when using data-bound controls in Windows Forms, but it can also be used to provide an easy way to manage the connection between your application and the underlying database tables, views and Stored Procedures. Learn more here: Data Adapter in ADO.NET.
5. DataSet Class
The DataSet is the heart of ADO.NET. The DataSet is essentially a collection of DataTable objects. In turn each object contains a collection of DataColumn and DataRow objects. The DataSet also contains a Relations collection that can be used to define relations among Data Table Objects.
How to Connect to a Database using ADO.NET
Now let us learn how to connect to a database using ADO.NET. To create a connection, you must be familiar with connection strings. A connection string is required as a parameter to SQLConnection. A ConnectionString is a string variable (not case sensitive).
This contains key and value pairs, like provider, server, database, userid and word as in the following:
Server=»nameof the server or IP Address of the server»
Database=»name of the database»
userid=»user name who has permission to work with database»
word=»the word of userid»
Example
SQL AuthenticationString constr=»server=.;database=institute;user id=rakesh;word=abc@123″;
Or:
String constr=»data source=.;initial catalog=institute;uid=rakesh;pwd=abc@213″;
Windows Authentication
String constr=»server=.;database=institute;trusted_connection=true»
Or:
String constr=»server=.;initial catalog=institute;integrated security=true»
How to retrieve and display data from a database
- Create a SqlConnection object using a connection string.
- Handle exceptions.
- Open the connection.
- Create a SQLCommand. To represent a SQLCommand like (select * from studentdetails) and attach the existing connection to it. Specify the type of SQLCommand (text/storedprocedure).
- Execute the command (use executereader).
- Get the Result (use SqlDataReader). This is a forwardonly/readonly dataobject.
- Close the connection
- Process the result
- Display the Result
The following is code for connecting to a SQL Database:

You must use the System.Data.SqlClient namespace to connect to a SQL Database. In the preceding code we are using the SqlConnection class, SqlCommand class and SqlDataReader class because our application is talking to SQL Server. SQL Server only understands SQL.
Code for connecting to Oracle Database
If you want to connect to an Oracle database, all you need to do is to change the connection class name from SqlConnection to OracleConnection Command class name from SqlCommand to OracleCommand and SqlDataReader to OracleDataReader and also in the beginning use the namespace System.Data.OralceClient.
This works for OleDb and ODBC also.
Thank You.
ADO.NET is a data access technology created by Microsoft. It helps .NET developers to connect to the database from C# code. This technology is a set of software components that developers use to access data and data services from a database.
ADO.NET stands for ActiveX Data Objects. It acts as a layer that connects the database and C# code.
Before you start this tutorial, make sure you are comfortable with the basics of C# and SQL. If you aren’t, check out my tutorials on C# and MS SQL Server Basics.
In this ADO.NET tutorial, let’s see how we can implement ADO.NET and connect the C# code to the MS SQL Server database using Visual Studio.
Let’s jump right in.
Steps to Create a Database and Table in ADO.NET
Open Visual Studio and create a new C# console-based project.
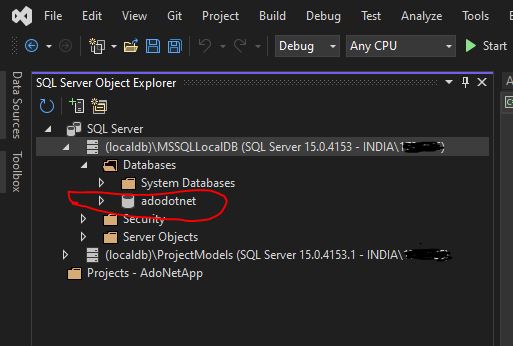
Navigate to the following options:
View -> SQL Server Object Explorer -> SQLServer -> LocalDB -> Right Click -> New Query
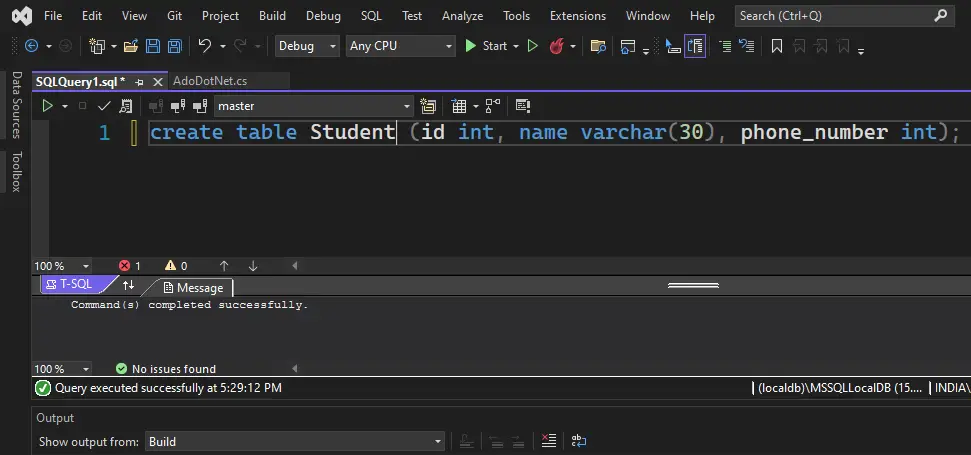
You can write SQL queries here. Write a query to create a database.
create database adodotnet;Now, let’s create a table in this database.
create table Student (id int, name varchar(30), phone_number int);Now, we have a table and a database. We can connect C# to this database and table using ADO.NET.
Let’s start writing the C# code.
Steps to Write ADO.NET Code
Let’s look at a rough template to see how we are connecting to the database and performing CRUD operations. These are the steps that we will follow for writing ADO.NET code in C#.
The first thing you need to do is to import the System.Data.SqlClient namespace.
using System.Data.SqlClient;
Now, create a connection object. You need to mention the data source, initial catalog, user id, and password for the database.
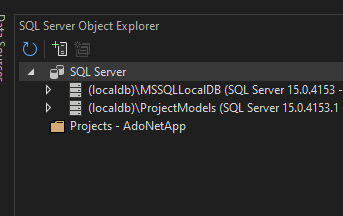
You can find the data source name in the following section in SQL Server Object Explorer.
The Initial Catalog is the name of the database you want to connect to. In our example, the database name is adodotnet.
The User id and Password are optional fields.
string connectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB;
Initial Catalog=adodotnet;
User id= UserName;
Password = Secret;
";
SqlConnection connectionObject = new SqlConnection(connectionString);Once you create a connection object, you need to open it.
connectionObject.Open();Now you can write an SQL query as a string and create an object of SqlCommand.
string sql = "insert into Student values(@id,'Bob',12345)";
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, connectionObject);Now, if your query is dynamic, you can pass your parameters to the query. In the above example, I have kept the variable @id for accepting the id value dynamically. Let’s add a parameter value to this variable.
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", 101);It is time to execute the query. We can execute an SQL query using three methods. We will see when to use which method.
Let’s execute the SQL query using ExecuteNonQuery(). We use this method to execute any SQL statements if we don’t want any result set to be returned.
command.ExecuteNonQuery();If you want the result set to be returned as an array of DataSet, then use the ExecuteReader() command and store the array in an SqlDataReader object. You can loop through this array and get values one by one.
SqlDataReader r = command.ExecuteReader();
while (r.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(r["id"]);
Console.WriteLine(r["name"]);
}
r.Close();If you want the SQL query to return a single value, then use the ExecuteScalar() method.
var maxId = command.ExecuteScalar();You can use any of the three methods mentioned above based on your requirement to execute the query.
Once the query is executed, you can print the success message or perform the necessary operations.
Console.WriteLine("Success message!");Once all the database-related tasks are done, you can close the connection object.
connectionObject.Close();Note: I would suggest using try-catch blocks when you write ADO.NET code so that you can handle all the exceptions properly.
Complete Code for ADO.NET CRUD Operations
Given below is the code to perform basic CRUD operations using ADO.NET in Visual Studio with MS SQL Server database.
using System;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace AdoDotNetApp
{
public class AdoDotNetBasics
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SqlConnection conn = createConnection();
conn.Open();
Student bob = new Student(101, "Bob", 198765);
Student ann = new Student(102, "Ann", 112211);
insertData(conn, bob);
insertData(conn, ann);
updateData(conn,101);
deleteData(conn, 101);
deleteData(conn,102);
getData(conn);
conn.Close();
Console.WriteLine("Connection closed.");
}
static SqlConnection createConnection()
{
try
{
string connectionString = @"Data Source=(localdb)\MSSQLLocalDB;
Initial Catalog=adodotnet;";
SqlConnection connectionObject = new SqlConnection(connectionString);
Console.WriteLine("Connection established.");
return connectionObject;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
return null;
}
}
static void insertData(SqlConnection conn, Student s)
{
try
{
string sql = "insert into Student values(@id,@name,@phone);";
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, conn);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", s.id);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@name", s.name);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@phone", s.phone);
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.WriteLine("Data inserted successfully.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
static void updateData(SqlConnection conn, int id)
{
try
{
string sql = "update Student set name='John' where id=@id;";
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, conn);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", id);
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.WriteLine("Data updated successfully.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
static void getData(SqlConnection conn)
{
try
{
string sql = "select * from Student;";
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, conn);
SqlDataReader r = command.ExecuteReader();
while (r.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine(r["id"]);
Console.WriteLine(r["name"]);
}
// for retrieving a single value, use:
// var maxId = command.ExecuteScalar();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
static void deleteData(SqlConnection conn, int id)
{
try
{
string sql = "delete from Student where id=@id;";
SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sql, conn);
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@id", id);
command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.WriteLine("Data deleted successfully.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e);
}
}
}
class Student
{
public int id;
public string name;
public int phone;
public Student(int id, string name, int phone)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
}
}
}
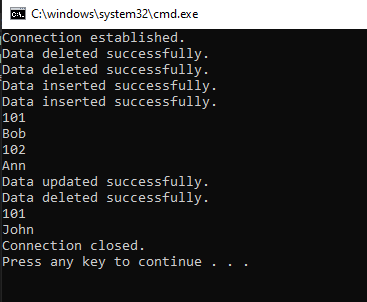
Output:Question 1: Introduction to ADO.NET
Answer
Definition: ADO is a rich set of classes, interfaces, structures, and enumerated types that manage data access from various types of data stores.
- Enterprise applications handle a large amount of data. This data is primarily stored in relational databases, like Oracle, SQL Server, Access, and so on. These databases use Structured Query Language (SQL) for retrieval of data.
- To access enterprise data from a .NET application, an interface was needed. This interface acts as a bridge between an RDBMS system and a .Net application. ADO.NET is such an interface that is created to connect .NET applications to RDBMS systems.
- In the .NET framework, Microsoft introduced a new version of Active X Data Objects (ADO) called ADO.NET. Any .NET application, either Windows-based or web-based, can interact with the database using a rich set of classes of the ADO.NET library. Data can be accessed from any database using connected or disconnected architecture.
- There were many data access technologies available prior to ADO.NET, primarily the following:
- Open Database Connectivity (ODBC)
- Data Access Objects (DAO)
- Remote Data Objects (RDO)
- Active X Data Objects (ADO)
- ADO is a simple component-based object-oriented interface to access data whether relational or non-relational databases. It is a successor of DAO and RDO.
- ADO reduces the number of objects. Their properties, methods, and events.
- ADO is built on COM; specifically Activex
- ADO supports universal data access using Object Linking and Embedding for DataBases (OLEDB). This means that there are no restrictions on the type of data that can be accessed.
ADO.NET provides mainly the following two types of architectures:
- Connected Architecture
- Disconnected Architecture
Question 2: ADO.NET Architecture
Answer
Connected and Disconnected Architectures
The following figure shows how to work with the connected and disconnected architectures.
Connected Architecture
- In the connected architecture, connection with a data source is kept open constantly for data access as well as data manipulation operations.
- The ADO.NET Connected architecture considers mainly three types of objects.
- SqlConnection con;
- SqlCommand cmd;
- SqlDataReader dr;
Disconnected Architecture
- Disconnected is the main feature of the .NET framework. ADO.NET contains various classes that support this architecture. The .NET application does not always stay connected with the database. The classes are designed in a way that they automatically open and close the connection. The data is stored client-side and is updated in the database whenever required.
- The ADO.NET Disconnected architecture considers primarily the following types of objects:
- DataSet ds;
- SqlDataAdapter da;
- SqlConnection con;
- SqlCommandBuilder bldr;
1. Connection Object and Connection string
Connection Object
- One of the first ADO.NET objects is the connection object, that allows you to establish a connection to a data source.
- The connection objects have the methods for opening and closing connections, for beginning a transaction of data.
- The .Net Framework provides two types of connection classes:
The sqlconnection object, that is designed specially to connect to Microsoft SQL Server and the OleDbConnection object, that is designed to provide connection to a wide range of databases, such as Microsoft Access and Oracle. - A connection is required to interact with the database. A Connection object helps to identify the database server name, user name and password to connect to the database. The Connection object is used by commands on the database.
- A Connection object has the responsibility of establishing a connection with the data store.
- How to use the Sqlconnection object:
- Instantiate the SqlConnection class.
- Open connection.
- Pass the connection to ADO.NET objects.
- Perform the database operations with ADO.NET object.
- Close the connection.
Connection String
| No. | Connection String Parameter Name | Description |
| 1 | Data Source | Identify the server. Could be a local machine, machine domain name, or IP Address. |
| 2 | Initial Catalog | Data base name. |
| 3 | Integrated Security | Set to SSIP to make a connection with the user’s window log in. |
| 4 | User ID | Name of user configured in SQL Server. |
| 5 | Password | Password matching SQL Server User ID |
The connection string is different for each of the various data providers available in .NET 2.0. There are different connection strings for the various types of data sources. You can find a list of all the available providers for creating a connection in a table:
| No | Provider | Description |
| 1 | System.Data.SqlClient | Provides data for Microsoft SQL Server |
| 2 | System.Data.OleDb | Provides data access for data sources exposed using OLE DB |
| 3 | System.Data.Odbc | Provides data access for data source exposed using ODBC. |
| 4 | System.Data.OracleClient | Provides data access for Oracle. |
Example
- SqlConnection con;
- con = new SqlConnection(«Server=Krushna;Database=Anagha;Uid=sa;Pwd=sa»);
2. Command Object
- A Command object executes SQL statements on the database. These SQL statements can be SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. It uses a connection object to perform these actions on the database.
- A Connection object specifies the type of interaction to perform with the database, like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
- A Command object is used to perform various types of operations, like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE on the database.
- SELECT
- cmd =new SqlCommand(«select * from Employee», con);
- INSERT
- cmd = new SqlCommand(«INSERT INTO Employee(Emp_ID,
- Emp_Name)VALUES (‘» + aa + «‘,‘» + bb + «‘)», con);
- UPDATE
- SqlCommand cmd =new SqlCommand(«UPDATE Employee SET
- Emp_ID =‘» + aa + «‘, Emp_Name =‘» + bb + «‘ WHERE
- Emp_ID = ‘» + aa + «‘«, con);
- DELETE
- cmd =new SqlCommand(«DELETE FROM Employee where
- Emp_ID=‘» + aa + «‘«, con);
- A Command object exposes several execute methods like:
- ExecuteScaler()
Executes the query, and returns the first column of the first row in the result set returned by the query. Extra columns or rows are ignored. - ExecuteReader()
Display all columns and all rows in the client-side environment.
In other words, we can say that they display datatables client-side. - ExecuteNonQuery()
Something is done by the database but nothing is returned by the database.
3. Data Reader Object
A DataReader object is used to obtain the results of a SELECT statement from a command object. For performance reasons, the data returned from a data reader is a forward-only stream of data. This means that the data can be accessed from the stream in a sequential manner. This is good for speed, but if data needs to be manipulated then a dataset is a better object to work with.
Example
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- It is used in Connected architecture.
- Provide better performance.
- DataReader Object has Read-only access.
- DataReader Object Supports a single table based on a single SQL query of one database.
- While DataReader Object is Bind to a single control.
- DataReader Object has Faster access to data.
- DataReader Object Must be manually coded.
- we can’t create a relation in the data reader.
- whereas Data reader doesn’t support.
- The data reader communicates with the command object.
- DataReader can not modify data.
4. Data Adapter Object
- A Data Adapter represents a set of data commands and a database connection to fill the dataset and update a SQL Server database.
- A Data Adapter contains a set of data commands and a database connection to fill the dataset and update a SQL Server database. Data Adapters form the bridge between a data source and a dataset.
- Data Adapters are designed depending on the specific data source. The following table shows the Data Adapter classes with their data source.
| Provider-Specific Data Adapter classes | Data Source |
| SqlDataAdapter | SQL Server |
| OledbDataAdapter | OLE DB provider |
| OdbcDataAdapter | ODBC driver |
| OracleDataAdapter | Oracle |
Provider-Specific Data Adapter classes
Data Source
- A Data Adapter object accesses data in a disconnected mode. Its object contains a reference to a connection object.
- It is designed in a way that implicitly opens and closes the connection whenever required.
- It maintains the data in a DataSet object. The user can read the data if required from the dataset and write back the changes in a single batch to the database. Additionally, the Data Adapter contains a command object reference for SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations on the data objects and a data source.
- A Data Adapter supports mainly the following two methods:
- Fill ()
The Fill method populates a dataset or a data table object with data from the database. It retrieves rows from the data source using the SELECT statement specified by an associated select command property.
The Fill method leaves the connection in the same state as it encountered it before populating the data. If subsequent calls to the method for refreshing the data are required then the primary key information should be present. - Update ()
The Update method commits the changes back to the database. It also analyzes the RowState of each record in the DataSet and calls the appriopriate INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements.
A Data Adapter object is formed between a disconnected ADO.NET object and a data source. - SqlDataAdapter da=new SqlDataAdapter(«Select * from Employee», con);
- da.Fill(ds,«Emp»);
- bldr =new SqlCommandBuilder(da);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[«Emp»];
Example
5. DataSet Object
- In the disconnected scenario, the data retrieved from the database is stored in a local buffer called DataSet. It is explicitly designed to access data from any data source. This class is defined in the System.Data namespace.
- A Data Set object is an in-memory representation of the data. It is specially designed to manage data in memory and to support disconnected operations on data.
- A Data Set is a collection of DataTable and DataRelations. Each DataTable is a collection of DataColumn, DataRows, and Constraints.
- A DataTable, DataColumn, and DataRows could be created as follows.
Example
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- DataColumn col =new DataColumn();
- Dt.columns.Add(col2);
- DataRow row = dt.newRow();
- It is used in a disconnected architecture.
- Provides lower performance.
- A DataSet object has read/write access.
- A DataSet object supports multiple tables from various databases.
- A DataSet object is bound to multiple controls.
- A DataSet object has slower access to data.
- A DataSet object is supported by Visual Studio tools.
- We can create relations in a dataset.
- A Dataset supports integration with XML.
- A DataSet communicates with the Data Adapter only.
- A DataSet can modify data.
6. Command Builder Object
- Automatically generates insert, update, delete queries using the SelectCommand property of a DataAdapter.
- A Command Builder Object is used to build commands for data modification from objects based on a single table query. CommandBuilders are designed depending on the specific data source. The following table shows the CommandBuilder classes with their data source.
| Provider-Specific Data Adapter classes | Data Source |
| SqlDataAdapter | SQL Server |
| OledbDataAdapter | OLE DB provider |
| OdbcDataAdapter | ODBC driver |
| OracleDataAdapter | Oracle |
Example
- da = new SqlDataAdapter(«Select * from Employee», con);
- ds = new DataSet();
- da.MissingSchemaAction = MissingSchemaAction.AddWithKey;
- da.Fill(ds, «Emp»);
- bldr = new SqlCommandBuilder(da);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[«Emp»];
Question 3: Differences Between DataReader and DataSet
Answer
| No | Data Reader | DataSet |
| 1 | Used in a connected architecture | used in a disconnected architecture |
| 2 | Provides better performance | Provides lower performance |
| 3 | DataReader object has read-only access | A DataSet object has read/write access |
| 4 | DataReader object supports a single table based on a single SQL query of one database | A DataSet object supports multiple tables from various databases |
| 5 | A DataReader object is bound to a single control | A DataSet object is bound to multiple controls |
| 6 | A DataReader object has faster access to data | A DataSet object has slower access to data |
| 7 | A DataReader object must be manually coded | A DataSet object is supported by Visual Studio tools |
| 8 | We can’t create a relation in a data reader | We can create relations in a dataset |
| 9 | Whereas a DataReader doesn’t support data reader communicates with the command object. | A Dataset supports integration with XML Dataset communicates with the Data Adapter only |
| 10 | DataReader cannot modify data | A DataSet can modify data |
Question 4: DataView Object
Answer
- A DataView is the same as a read-only mini-dataset.
- You typically load only a subset into a DataView.
- A DataView provides a dynamic view of data. It provides a datarow using the DataView.
Example
Add two buttons and a DataGridView control. Change the text of the first button to sort by city and that of button2 to only select records in Mexico and add the code in form.cs.
Form Design
Coding Part
- SqlConnection con;
- SqlCommand cmd;
- SqlDataReader dr;
- public DataTable GetTable()
- {
- con = new SqlConnection(«Data Source=.\\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=information;Integrated Security=True;Pooling=False»);
- con.Open();
- cmd = new SqlCommand(«select * from Customers», con);
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
- con.Close();
- return dt;
- }
Form1_Load
- dataGridView1.DataSource = GetTable().DefaultView;
ShortByCity_Click
- DataView dv = new DataView(GetTable());
- dv.Sort = «City ASC»;
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dv;
OnlyInMexico_Click
- DataView dv = new DataView(GetTable());
- dv.RowFilter = «Country = ‘Mexico'»;
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dv;
- At the click of the sort by city button, the data already in the DataGridView control is sotred dy city.
- On clicking the second button, only the records in Mexico are displayed in the DataGridView control. The output after clicking the only in Mexico button is as the Mexico button.
Working With System.Data.SqlClient and System.Data.Oledb
Program: Design a simple Winform for accepting the details of Employee. Using the connected architecture of ADO.NET, perform the following operations:
- Insert record.
- Search record.
- Update record.
- Delete record.
- Form Design
- Coding Part
Step 1: add namespace using System.Data.SqlClient;for SQL dataBase.Step 2: Create a connection object.
- SqlConnection con;
- SqlCommand cmd;
- SqlDataReader dr;
Step3: Form1_Load
- con =new SqlConnection(«Data Source=.\\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=information;Integratedecurity=True;Pooling=False»);
- private void Display()
- {
- con.Open();
- cmd =new SqlCommand(«select * from Employee», con);
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
- con.Close();
- }
Insertbtn_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string bb = textBox2.Text;
- int cc = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
- cmd =new SqlCommand(«INSERT INTO Employee(Emp_ID, Emp_Name,Salary)VALUES (‘» + aa +«‘,'» + bb + «‘,'» + cc + «‘)», con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record inserted:»);
- con.Close();
- Display();
Deletebtn_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- cmd =new SqlCommand(«DELETE FROM Employee where Emp_ID='» + aa + «‘», con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record Delete:»);
- con.Close();
- Display();
Updatebtn_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string bb = textBox2.Text;
- int cc = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
- string abc = «UPDATE Employee SET Emp_ID ='» + aa + «‘, Emp_Name ='» + bb + «‘,Salary ='» + cc + «‘ WHERE Emp_ID = ‘» + aa +«‘»;
- SqlCommand cmd =new SqlCommand(abc, con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record updated:»);
- con.Close();
- Display();
Displaybtn_Click
- Display();
Searchbtn_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string abc = «SELECT Emp_ID,Emp_Name,Salary FROM Employee where Emp_ID='» + aa +«‘»;
- cmd =new SqlCommand(abc, con);
- MessageBox.Show(«one record search:»);
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt =new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
- con.Close();
Totalrecordbtn_Click
- con.Open();
- cmd = new SqlCommand(«select Count(*) from Employee», con);
- int a = (int)cmd.ExecuteScalar();
- label4.Text = «Total Record:—> « + a.ToString();
- con.Close();
Exit_Click
- Application.Exit();
Program: Design a Simple Winform for accepting the details of an Employee. Using the connected architecture of ADO.NET, perform the following operations:
- Insert record.
- Search record.
- Update record.
- Delete record.
Form Design
Coding Part
Step 1: add namespace using System.Data.Oledb; for access Database.
Step 2: Create connection object.
- OleDbConnection con;
- OleDbCommand cmd;
- OleDbDataReader dr;
Step 3: Form1_Load
- con = new OleDbConnection(«Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=C:\\Documents and Settings\\Admin\\Desktop\\Ado Connected Demo\\db1.mdb»);
- private void display()
- con.Open();
- cmd = new OleDbCommand(«select * from Employee»,con);
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
- con.Close();
Display_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string bb = textBox2.Text;
- int cc = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
- cmd = new OleDbCommand(«INSERT INTO Employee(Emp_ID, Emp_Name,Salary) VALUES (‘» + aa + «‘,'» + bb + «‘,'» + cc + «‘)», con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record inserted:»);
- con.Close();
- display();
Delete_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- cmd = new OleDbCommand(«DELETE FROM Employee where Emp_ID='» + aa + «‘», con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record Delete:»);
- con.Close();
- display();
update_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string bb = textBox2.Text;
- int cc = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
- string abc = «UPDATE Employee SET Emp_ID ='» + aa + «‘, Emp_Name ='» + bb + «‘, Salary ='» + cc + «‘ WHERE Emp_ID = ‘» + aa + «‘»;
- OleDbCommand cmd = new OleDbCommand(abc, con);
- cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
- MessageBox.Show(«one record updated:»);
- con.Close();
- display();
Find_Click
- con.Open();
- int aa = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
- string abc = «SELECT Emp_ID,Emp_Name,Salary FROM Employee where Emp_ID='» + aa + «‘»;
- cmd = new OleDbCommand(abc, con);
- MessageBox.Show(«one record search:»);
- dr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
- DataTable dt = new DataTable();
- dt.Load(dr);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = dt;
- con.Close();
Exit_Click
Application.Exit();
Program: Design a simple Winform for accepting the details of an Employee. Using the disconnected architecture of ADO.NET, perform the following operations.
- Insert record.
- Display record.
- Update record.
- Delete record
Form Design
Coding Part
Step 1: add namespace using System.Data.SqlClient;for SQL dataBase.
Step 2: Create connection object.
- DataSet ds;
- SqlDataAdapter da;
- SqlConnection con;
- SqlCommandBuilder bldr;
Step 3: Form1_Load
- con = new SqlConnection(«Data Source=.\\sqlexpress;Initial Catalog=information;IntegratedSecurity=True;Pooling=False»);
- private void display()
- da = new SqlDataAdapter(«Select * from Employee», con);
- ds = new DataSet();
- da.MissingSchemaAction = MissingSchemaAction.AddWithKey;
- da.Fill(ds, «Emp»);
- bldr = new SqlCommandBuilder(da);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[«Emp»];
Display_Click
- DataRow drnew = ds.Tables[«Emp»].NewRow();
- drnew[0] = textBox1.Text;
- drnew[1] = textBox2.Text;
- drnew[2] = textBox3.Text;
- ds.Tables[«Emp»].Rows.Add(drnew);
- da.Update(ds, «Emp»);
- MessageBox.Show(«Record added»);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[«Emp»];
Delete_Click
- DataRow row = ds.Tables[«Emp»].Rows.Find(Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text));
- row.Delete();
- da.Update(ds, «Emp»);
- MessageBox.Show(«Record Deleted»);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[«Emp»];
Update_Click
- DataRow dr = ds.Tables[0].Rows.Find(textBox1.Text);
- dr[«Emp_Name»] = textBox2.Text;
- dr[«Salary»] = textBox3.Text;
- da.Update(ds, «Emp»);
- MessageBox.Show(«updated..»);
- dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[0];
FirstRcd_Click
- this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position = 0;
LastRcd_Click
- this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position = ds.Tables[0].Rows.Count — 1;
NextRcd_Click
- if (this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position > 0)
- {
- this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position -= 1;
- }
PreviousRcd_Click
- if (this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position < ds.Tables[0].Rows.Count — 1)
- {
- this.BindingContext[ds.Tables[0]].Position += 1;
- }